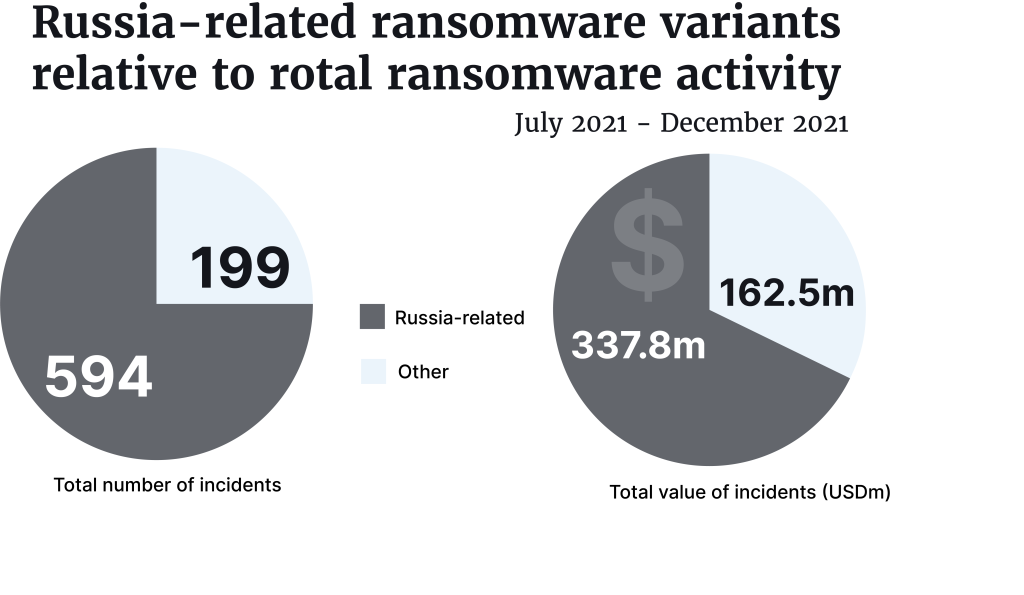
Ransomware is continuing to pose a significant threat to US critical infrastructure sectors, businesses, and the public, the new Financial Trend Analysis from The Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) shows. And Russia is linked to almost 75% of attacks.
Since 2020, ransomware-related incidents have increased substantially, with 602 incidents filed in 2020 and at least 1,251 in 2021. The value of the incidents cost roughly $527m in 2020 and $886m in 2021, an increase of 68%. The report picks up on increasing ransomware trends in Bank Secrecy Act Data (BSA) filings.
Serious threat
Most ransomware attacks came during the second half of 2021, when 793 incidents were reported. Almost 75% were related to Russia or Russian-speaking countries. FinCEN identified 84 types of ransomware variants, 49 connected with Russian cyber actors.
“Today’s report reminds us that ransomware, including attacks perpetrated by Russian-linked actors, remain a serious threat to our national and economic security,” said FinCEN Acting Director Himamauli Das.
“It also underscores the importance of BSA filings, which allow us to uncover trends and patterns in support of whole-of-government efforts to prevent and combat ransomware attacks. Financial institutions play a critical role in helping to protect the United States from ransomware-related threats simply by fulfilling their BSA compliance obligations.”
FinCEN is working proactively against cybercrime and is making the work a priority. It issued an anti-money laundering and countering the financing of terrorism (AML/CFT) policy in June 2021. The organisation has gathered ransomware-related BSA data since January 1, 2011, and up to January 31, 2022, a total of 3,193 BSA filings have been reported, costing roughly $2.31bn.
The report is issued as a requirement of the Anti-Money Laundering Act 2020.
The Bank Secrecy Act (BSA)
The Currency and Foreign Transactions Reporting Act of 1970 – which legislative framework is commonly referred to as the “Bank Secrecy Act” (BSA) – requires US financial institutions to assist US government agencies to detect and prevent money laundering.
Source: fincen.gov






