Hackers are producing more effective phishing attacks by using improved Generative AI and Large Language Models (LLMs), Trustwave SpiderLabs’ 2023 Financial Services Sector Threat Landscape report shows.
During the last year, Trustwave SpiderLabs has observed developments in how email-based threats have been delivered, their techniques and themes, and how certain brands have been used to produce attacks in financial services. And it still continues to be one of the most effective methods for attackers to gain an initial foothold in financial services as well as other organizations.
A staggering 92% of all organizations say that they have been victims of successful phishing attacks in the last year, and 99% of cybersecurity leaders are said to be stressed about email security.
“Use of LLM technology makes the crafting of phishing emails even easier, more compelling, highly personalized, and harder to detect.”
Trustwave SpiderLabs
Successful attacks are very dependent on the ‘quality’ of their look and style and Trustwave SpiderLabs has noticed, with concern, that the use of Generative AI and LLMs is improving the quality of such attacks.
“The quick maturity and expanded use of LLM technology makes the crafting of phishing emails even easier, more compelling, highly personalized, and harder to detect,” Trustwave SpiderLabs said.
WormGPT and FraudGPT
More deepfakes are being deployed, too, as a result of more sophisticated technology.
“Lately, we have seen the emergence of LLMs like WormGPT and FraudGPT on underground forums, highlighting the potential cybersecurity risks posed by their criminal use,” the report says, warning that detecting phishing attempts is getting harder because of their increased speed and quality. Security vendors will need to adjust their detection and response capabilities accordingly.
“WormGPT and FraudGPT can craft convincing phishing emails without many of the red flags that we teach users to identify phishing emails by, including items like picking out misspellings, grammar mistakes, and general clumsiness of writing that may indicate that the author is not a native speaker.”
Microsoft and American Express
The increase in ransomware attacks within the financial services industry “underscores the significant enhancement in adversaries’ ability to conduct large-scale attacks,” the report concludes. It says the ransomware-as-a-service model lets hackers scale their attacks and achieve widespread impact. Coming second behind the health care industry, a data breach within the financial sector is estimated to cost and average of $5.9m – compared to the industry average of $4.4m, according to a report from the Ponemon Institute.
Microsoft was the most spoofed brand in phishing attacks (52%), followed by DocuSign (10%), and American Express (8%). For emails with malicious attachments, American Express was found to be the most spoofed brand (24%), DHL second (21%), and Microsoft third (15%).
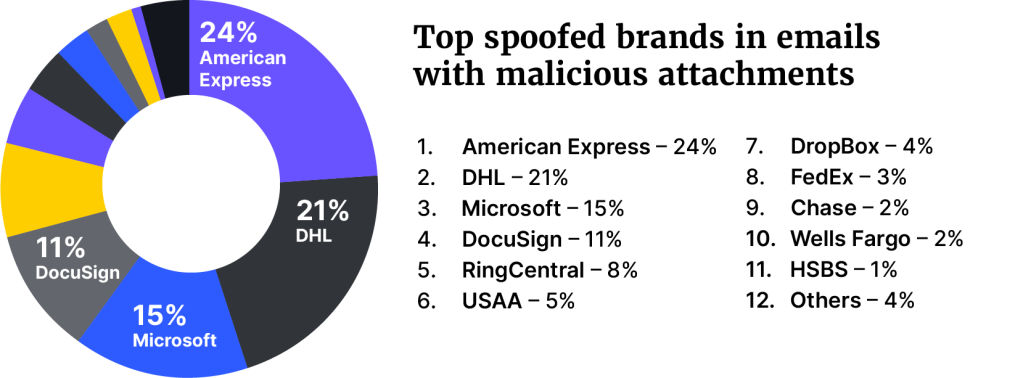
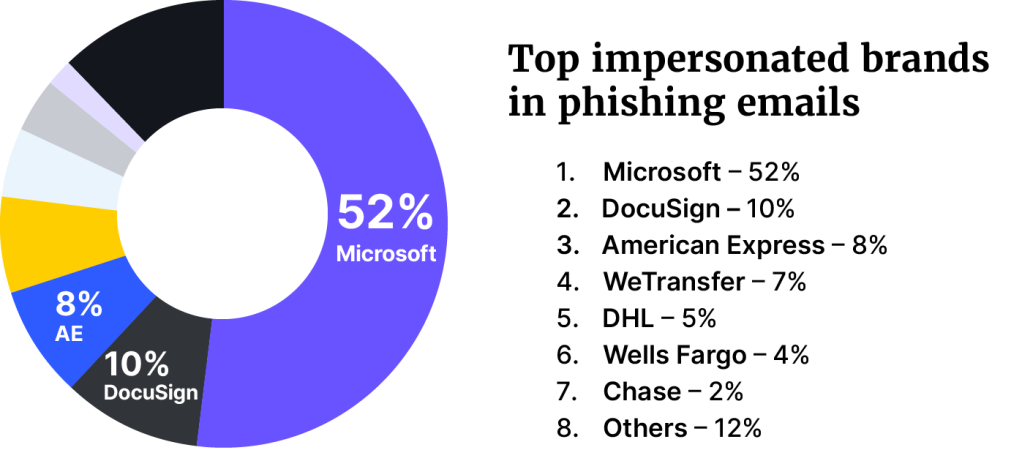
The research found 78% of all malicious attachments came through HTML attachments. These attachments were then used for credential phishing, redirectors, and HTML smuggling. It is notable is that about a third of the HTML files employed obfuscation as a means of defense evasion.
The most common themes of the emails related to voicemail notifications, payment receipts, purchase orders, remittances, bank deposits, and quotation requests.
The most common phishing themes, without malicious attachments, were around “Urgent Action” themes, mailboxrelated alerts, document sharing, e-signing, account-related alerts, missed communications, meeting-related notifications, and payment/invoice-related alerts.
Attacks via third-party vendors
Attacks on third-party software and services are another point of concern. There has been a sharp rise in successful attacks against supplier-based vendors, targeting the “weak side” of an organization. Attacks can come through third-party code, APIs, vendors, support providers, and other managed services.
“Through this approach, attackers can access the targeted company’s data and infrastructure even though the company itself may have a relatively high security maturity,” Trustwave SpiderLabs explains, and says that they have seen hundreds of organizations being affected by these types of attacks.
Some of the recent attacks include SolarWinds, 3CX and MOVEit – which is currently under investigation by the SEC over massive breaches.
Even though this isn’t a unique threat just connected to financial services alone, Trustwave SpiderLabs says that since almost everything is more or less connected “the issue is exacerbated” and that, “One weak link in the chain can lead to grave consequences for the organization”.
Customer cybersecurity guidance
Besides making sure that your employees have good cyber practises, Trustwave SpiderLab also highlighted ensuring customer safety, by implementing:
- Consumer security education: Inform customers about the dangers of phishing and malware threats, and educate them on safe online practices which include recognizing phishing attempts.
- Security controls: Set robust security measures to safeguard accounts with controls such as encryption, multi-factor authentication (MFA), human identification, penetration testing for consumer facing apps, and intrusion detection systems.
- Customer support and incident response: Set a support mechanism that alerts customers when a security incident has occurred, assist with changing passwords, securing compromized accounts, and provide guidance on reinforcing personal security practices.













